<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1, minimum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"
/>
<title>hello word</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: 'hello world',
content: 1,
}
},
mounted() {
setInterval(() => {
this.content++
}, 1000)
},
template: '<div>{{message}} {{content}}</div>',
}).mount('#root')
</script>
</html>
v-model多用于表单元素实现双向数据绑定(类似于 Angular 中的 ng-model)。
v-for格式:v-for="字段名 in(of) 数组 json"
循环数组或 JSON(类似于 Angular 中的 ng-repeat),需要注意从 Vue 2 开始取消了 $index。
v-show显示内容(类似于 Angular 中的 ng-show)。
v-hide隐藏内容(类似于 Angular 中的 ng-hide)。
v-if显示与隐藏(DOM 元素的删除添加,类似于 Angular 中的 ng-if,默认值为 false)。
v-else-if必须和 v-if 连用。
v-else必须和 v-if 连用,不能单独使用,否则会报错模板编译错误。
v-bind动态绑定,作用是及时对页面的数据进行更改。
v-on:click给标签绑定函数,可以缩写为 @,例如绑定一个点击函数。函数必须写在 methods 里面。
v-text解析文本。
v-html解析 HTML 标签。
v-bind:class三种绑定方法:
{red:isred}isred ? "red" : "blue"[{red: "isred"}, {blue: "isblue"}]v-once进入页面时只渲染一次,不再进行渲染。
v-cloak防止闪烁。
v-pre把标签内部的元素原位输出。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1, minimum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"
/>
<title>反转、显示/隐藏</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: 'hello world',
show: true,
}
},
methods: {
handleBtnClick1() {
this.message = this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
},
handleBtnClick2() {
this.show = !this.show
},
},
template: `
<div>
<span v-if="show">{{message}}</span>
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick1">反转</button>
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick2">显示/隐藏</button>
</div>
`,
}).mount('#root')
</script>
</html>
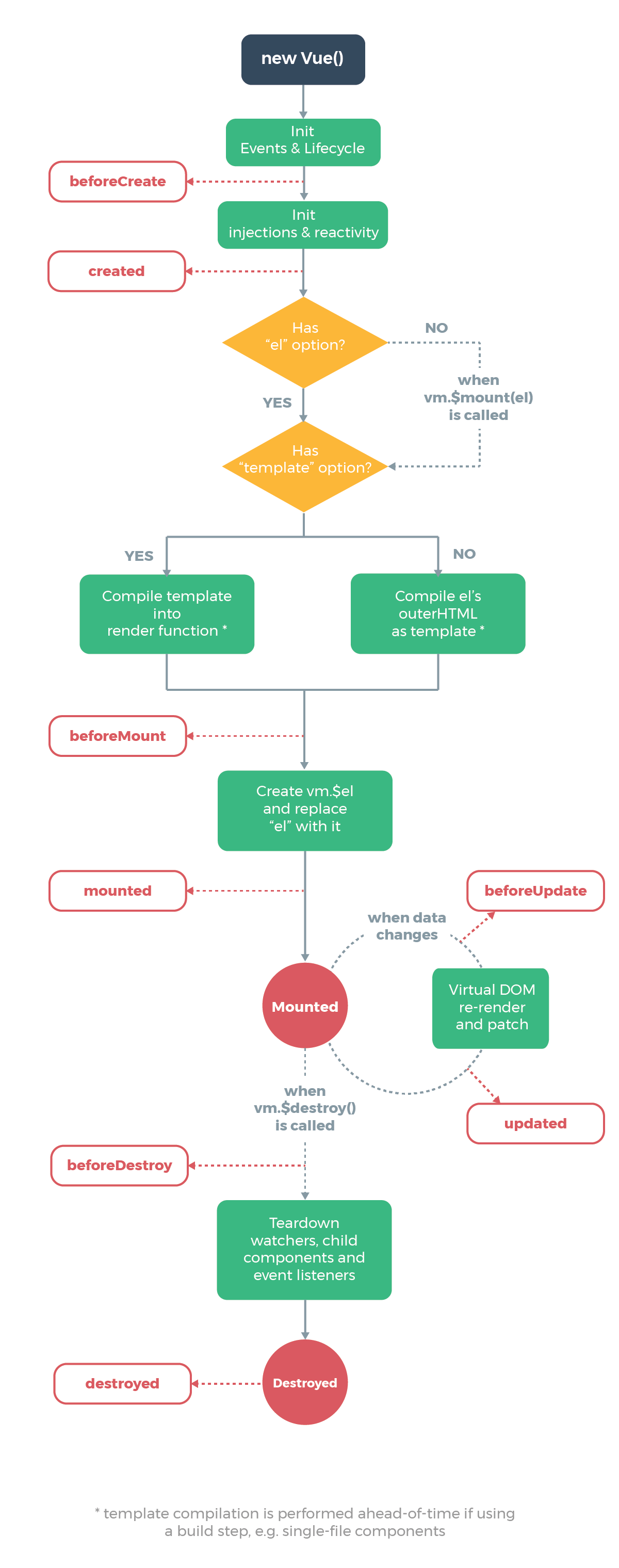
computed:当计算属性依赖的内容发生变更时,才会重新执行计算 methods:只要页面重新渲染,就会重新计算 watch:可以设置监听一个表达式或函数的结果变化,变化时执行回调函数,回调函数得到的参数为变化前后的新值和旧值,表达式支持单个变量和一个简单的属性访问路径,需要监听更复杂的表达式,需要使用函数取代。可以说 computed的底层实现是 watch。
computed 和 method 都能实现的一个功能,建议使用 computed,因为有缓存computed 和 watcher 都能实现的功能,建议使用 computed,因为更加简洁v-if 隐藏的原理:需要隐藏时(v-if为false时)直接删除而不显示 v-show 隐藏则是在需要隐藏时(v-show为false时)给该标签添加"display:none"属性让其不显示
v-show比较好。不会频繁创建删除标签操作,性能好。v-if v-else-if v-elsestop: 防止事件冒泡 prevent:取消默认事件 capture:捕获事件 self:只会触发自己范围内的事件,不会包含子元素 once:只执行一次的点击 passive:提早告诉,提高性能
组件是页面的一部分。
评论